
What Are Orphan Pages and How to Fix Them for Better Indexing & SEO
- accuindexcheck
- 0
- Posted on
Some pages on your website do not get the proper weight. Orphan pages are pages on your site that remain unconnected to other pages via internal links. Because there isn’t a straightforward path to these pages within the website’s structure, they are often missed by users amid regular navigation or search engine crawling.
In contrast to being indexed by Google and linked from your site, orphan pages receive no internal link equity and lie forgotten. While it is still possible to access an orphan page via its direct URL or external means, this lack of connectivity disables indexing and actively undermines SEO performance and user engagement.
Consider why orphan pages should matter to you and cater to these pages correctly so that you do not see your content go to waste, improve your site architecture, and ensure every valuable page carries out its assigned function in your digital strategy.
Why Orphan Pages Can Cause Problems
Initially, one might consider orphan pages to be innocuous; however, they are capable of precipitating serious issues in terms of your website’s visibility, SEO effectiveness, and user experience. Below are some of the chief reasons why fixing orphan pages should be on the top priority of your technical SEO checklist:
1. Negative Impact on Crawling and Indexing
Depending on internal links allow these crawlers to find new content. The orphan pages, without any link pointing to them, are usually skipped by these crawlers. Having a page in the sitemap won’t help if it does not have many internal links that point to it-it will be poorly found even by Google, thereby reducing its chances of getting indexed or ranked.
2. Lost Link Equity and SEO Value
Internal linking helps distribute ranking authority, or link equity, across pages on your website. An orphan page, therefore, would be deprived of this important SEO perk. If there is an exceptionally good page with worthy content, yet no other page links to it, then baying sites and search engines alike never know about its existence.
3. Poor User Experience and Content Discoverability
While users traverse your site, there is no way they might just happen upon an orphan page; hence useful or crucial content gets sidelined from view. This ensures a disjointed user journey that outputs people onto the website while peeking around or among the pages looking for an answer or information that is no longer found.
4. Missed Conversion Opportunities
Orphan pages might be for products, services, or lead magnets invisible to the standard flow of your site. This leads to loss in potential leads, sign-ups, or sales caused by the absence of links leading to the sales page where users might have found value.
Orphan Pages Can Be Harmful for SEO
If orphan pages remain unnoticed and unaddressed, they might, in silence, degrade your website’s search engine optimization. These unlinked pages thin out your site architecture and visibility among search engine result listings.
- Decreased Topical Relevance: Being in isolation from related content means that search engines will have difficulty understanding the context of such pages or associating them with main topics of your site.
- Crawl Budget Usage: Search engines have a finite number of pages they can crawl. A page that does not have good internal linkages needs no prioritization while others less important get crawled.
- Indexing Inconsistencies: There might be a random indexing of some pages considred orphans, whereas others are completely disregarded, causing inconsistent coverage in search results.
- Duplication & Cannibalization Risks: Hidden pages having overlapping content may compete against linked pages for keywords, thus diminishing their ranking potential.
- Less Engagement Metrics: Inbound users landing on orphan pages (e.g., External links) are more likely to bounce due to no path linking them to the rest of your content.
When Orphan Pages Are Not a Problem for Your Site
Orphan pages are not inherently bad. There are legitimate purposes they may serve: a thank-you page after a form submission, a temporary landing page for advertising, or an internal tool for limited access might not require internal links. Orphaning does not hurt a website’s SEO or usability as long as such pages do not need to rank in search engines or serve any navigational purpose.
How to Detect Orphan Pages on Your Website?
Detecting orphan pages helps boost SEO and guarantees that important content can be found by visitors and search engines. They are usually ignored, but the right tools and methods can help you find them. Here are four effective methods to identify orphan pages on your website:
1. Website Crawling Tools: You should run one or several crawling programs such as Screaming Frog, Sitebulb, or Ahrefs against your sitemap to locate those URLs which are apparently left off internal links. But before doing that make sure to check the pages indexing status with google indexing tools like accuindex, small seo tools and more.
2. Check with Google Analytics or Search Console: Search for those pages which might have gotten some hits, but from the main site, would have had their internal linking routes taken away. These pages might be orphaned, reachable only through direct URL visits or links from external websites.
3. Sitemap versus Crawl Report: Export your sitemap and your crawler’s URL list and place them in a spreadsheet for comparison. Any URL that exists in the sitemap but not in crawlable links is an orphan candidate.
4. Manual CMS Auditing: Have a look at your CMS manually and see if there are any published pages that aren’t linked in menus, categories, or other internal pages.
Ways to Fix Orphan Pages to Improve SEO Results
1. Integrate Orphan Pages into Your Site Structure
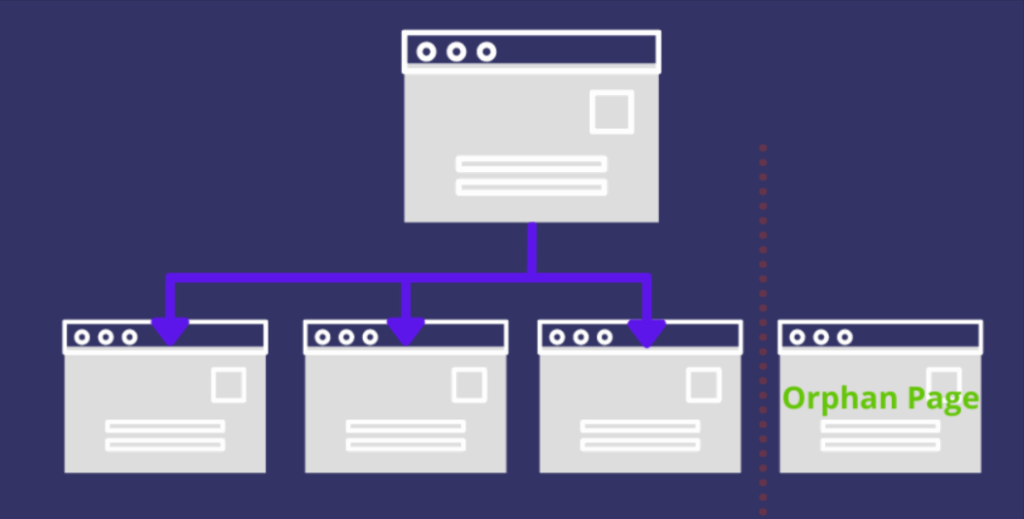
After finding worthy orphan pages, the next thing will be to link them to the internal linking structure. Such pages will be linked internally for users and search engines to have access to these pages and thereby it gains greater visibility and SEO weight.
Begin by looking for content elsewhere on your site- blogs, landing pages, or product pages-that would naturally relate to the orphan page. Place internal links in these articles, using anchor text that’s believable for both human readers and search engine robots.
If these orphan pages matter to users, add them to navigation menus, sidebar widgets, or category listings. When evergreens or very profitable content appears on an article page, footer links should be put on the page or maybe even a widget showing “related posts.”
2. Update the Sitemap and Robots.txt

For better indexing of the fixed orphan pages, always update your sitemap with the addition of the internal links. Be sure all newly connected pages are present in the sitemap; then, submit it to Google Search Console. This serves to further help search engines reach and crawl those pages.
Checked the robots.txt file, as well, to ascertain that some important pages are not blocked for inadvertent purposes from being crawled by search engine crawlers. If any URL was disallowed before, remove the rules for them so that they are properly indexed.
3. Use Contextual Linking Strategically
Context is key when fixing orphan pages; simply placing links there is insufficient. Internal links should be created from other highest-performing and relevant content in the site to these orphan pages. Doing so will give visibility to these orphan pages on both users and the search engine, and a transfer of link equity among authoritative pages will take place.
Links must be placed in contextually natural positions. The anchor text must describe and must be relevant to the target page so that search engines can develop an association between a pair of pages simultaneously improving user experience by letting users know what to expect on the other end after clicking the link.
4. Group Related Pages for Better Structure
In many cases, a cluster of multiple orphan pages on similar subject matter is indicative of content organization that is lax. Creating a dedicated hub or category page will consolidate the orphan pages into one coherent structure that is easy for the user and for search engines to follow.
This greatly improves navigation, thereby improving topical relevance and internal linking. Moreover, it tells search engines that your content is well organized around specific topics, which could improve SEO rankings in return. Each of the related pages will link back to the hub and thus constitute a network for increased discoverability and engagement among users.
5. Add Orphan Pages to Navigation or Pillar Pages
The deepest recesses of your website should never harbor any important content. Should you find an orphan page of value, whether informative, evergreen, or in support of your principal topics, it must be assigned a rightful place in the site structure.
- Main/Secondary Navigation: Orphan pages of paramount importance ought to be incorporated within header or footer menus so users can find them easily and search engines get a clear signal about their importance.
- Pillar or Core Content Clusters: Having valuable pillar pages on generic topics link to more specific orphan pages is a natural way in the flow of traffic. This also enhances topical relevance and internal SEO power.
- Resource Libraries or Archive Pages: In case your website has a blog archive, tools library, or downloads section, you can think about adding relevant orphan pages to boost their visibility.
When Should You Remove an Orphan Page?
If any page truly has out-of-date content, has no use, or duplicates content elsewhere, better to have it removed. Deleting these pages can certainly help cleaning up the site and improving crawls.
- Obsolete or meaningless content: Pages carrying obsolete data or irrelevant information should be forever done away with.
- Has no SEO value or traffic: If the page never gets any traffic and has no potential of ranking, it probably does nothing to add value.
- Use 301 redirect: Redirect an orphaned page with a few backlinks and some relevance to an active page to protect link equity.
FAQs
What constitutes an orphaned page in SEO terminology?
An orphaned page is a website page unlinked from any other pages within the site, hence is nearly impossible to reach in the course of a normal site navigation for either a user or a search engine.
Why then are orphan pages harmful to SEO?
They are hard to index and crawl, leech off the link equity, reduce their own visibility in content, and might damage the whole site structure and user experience.
How to identify orphan pages?
Utilizing crawlers like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs or even employing alternatives such as the Google Search Console should allow you to compare either your sitemap or indexed URL along with the list of internally linked pages.
Is it difficult to fix orphan pages?
Not really. You fix them by creating relevant internal links from other existing pages, updating sitemaps, and improving the site structure.
Does fixing orphan pages guarantee major SEO improvement?
Refurbishing such pages might not be the perfect SEO fix; it does, however, assist in crawlability, indexing, user navigation, all of which are good stuff in terms of SEO.
In Conclusion
An orphan page looks like a minor problem. However, it can weaken your SEO by having useful content isolated from the rest of your website. When an issue about an orphan page spot is made, ways are created to make sure that the content will be viewed, hence benefiting the content, the users, and search engines.
Connect orphan pages inside the internal link structure, update your sitemap anew, and restructure the website for visibility, crawlability, and SEO health. Conducting regular audits while keeping content well organized from the start helps keep your site well optimized, and user-friendly.