
Complete Google Indexing Process : How It Works & How to Fix Common Issues
- accuindexcheck
- 0
- Posted on
If you’ve ever published a website or blog post and waited anxiously for it to appear on Google, you’ve already started thinking about Google indexing. But how exactly does the Google indexing process work? And why do some pages show up quickly while others take days — or never appear at all?
In this article, we’ll walk through what indexing means, how it happens, how long Google indexing takes, common problems, and the best tools to monitor your progress — including a Google indexing checker and more.
What Page Indexing Means?
Indexing is the process by which search engines like Google store and organize content from web pages so they can show it in search results. After a page is discovered and crawled, Google analyzes its content and, if it meets quality guidelines, adds it to its index — a massive database of web pages. Only indexed pages are eligible to appear when someone searches on Google. Without indexing, your content remains invisible to search users.
What Is the Google Indexing Process?
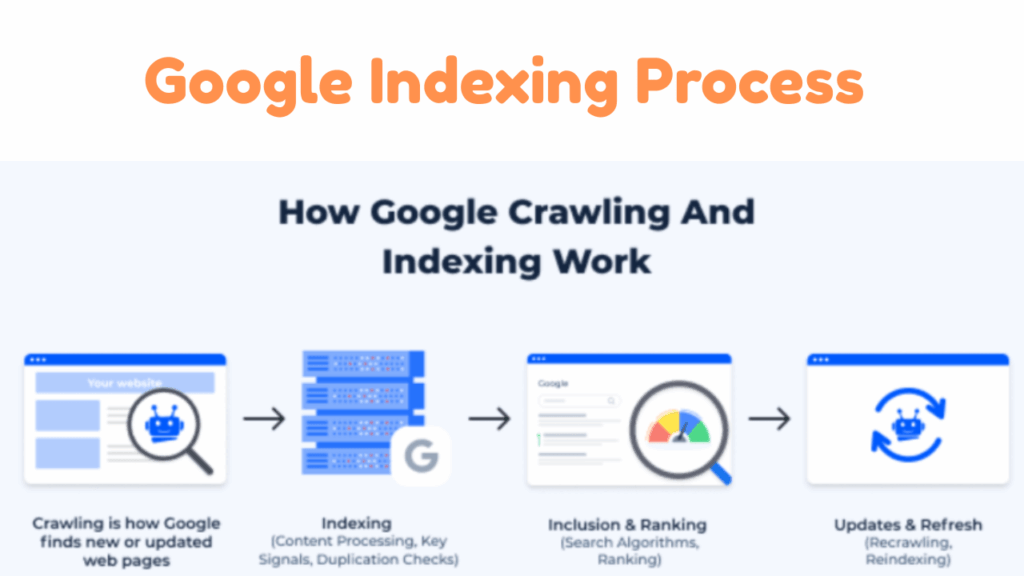
The Google indexing process is the way Google collects, stores, and organizes content from websites so it can be shown in search results.
It works in four key stages:
1. Discovery – How Google Reaches Your Web Page
Before Google can crawl or index a page, it must first discover that the page exists. This stage is known as discovery — and it’s the very first step in the Google indexing process.
Think of discovery as Google simply becoming aware that your page is out there on the internet. If a page isn’t discovered, Google won’t visit it, crawl it, or show it in search results. So, discovery is essential.
How Does Google Discover New Pages ?
- Following a Link : Googlebot finds your page by following a link from another website or from another page on your own site. Internal and external links help Google discover new content naturally.
- Reading Your XML Sitemap : If your site has an XML sitemap (usually at
yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml) and it’s submitted in Google Search Console, Google can use it to discover all listed pages, especially new or updated ones. - Manual URL Submission (Direct) : You can submit a specific URL directly in Google Search Console using the URL Inspection Tool. This tells Google to crawl and potentially index your page faster.
2. Crawling
Once Google has discovered your page, the next step is crawling. Crawling is when Googlebot (Google’s automated software or “bot”) visits your web page to read its content and code.
What Happens During Crawling?
Googlebot downloads the page and scans everything, including:
- Text and headings
- Images and alt tags
- Links (internal and external)
- HTML structure and metadata
- Scripts (like JavaScript or CSS)
This is how Google starts to understand what your page is about.
3. Processing – How Google Understands Your Page
After Google crawls your page, the next step is called processing. This is when Google analyzes the content and structure of your page to understand what it’s about and whether it’s worth indexing.
What Happens During Processing?
During this stage, Google reviews everything it gathered while crawling, including:
- Technical SEO – Google looks at canonical tags, structured data, redirects, and more.
- Text content – What topics you’re covering, how informative the content is, and which keywords are most important.
- Headings and structure – How well your content is organized (using H1, H2, etc.).
- Images and media – Whether images have descriptive alt text and how they contribute to the page.
- Meta tags – Such as the title tag and meta description, which help Google summarize your page.
- Links – Google checks both internal links (to other pages on your site) and external links (to and from other websites).
- Mobile usability – Is your page mobile-friendly and responsive?
- Page speed – Does your site load quickly?
4. Indexing – Storing Your Page in Google’s Search Database
Once Google finishes crawling and processing your page, the final step is indexing. This is when Google adds your page to its database — called the Google Index — so it can appear in search results.
What Determines If a Page Gets Indexed?
Google decides whether to index your page based on several factors:
- Content quality – The page must provide helpful, original, and relevant information.
- No duplicate content – Pages that copy from other sites or repeat existing content may be skipped.
- No spammy or thin pages – Pages with little useful content, too many ads, or poor structure may be ignored.
- No technical blocks – If your page has a
noindextag or is blocked in your robots.txt file, it won’t be indexed.
How to Check If Your Page Is Indexed
You can check if a page is indexed in two easy ways:
Google Search
Type: site:yourdomain.com/page-url
If it shows up in results, it’s indexed.
How Long Does Google Indexing Take?
This is one of the most common questions: How long does Google indexing take?
The answer depends on several factors:
| Page Type | Indexing Time |
|---|---|
| Brand-new page with no links | Several days to weeks |
| Page submitted via Search Console | A few hours to 1–2 days |
| Popular page with strong internal links | A few hours |
| Page with issues (slow, low content, errors) | Might never index |
So while some pages get indexed quickly, others may take days — or not be indexed at all unless you fix certain problems.
Common Google Indexing Issues
Even if your page is published and accessible, Google indexing issues can stop it from appearing in search results.
Here are the most common reasons:
1. Noindex Tag
A noindex tag in the page code tells Google to ignore the page. This is often added by mistake.
2. Blocked by Robots.txt
Your site’s robots.txt file may block Google from crawling some or all of your pages.
3. Slow Page Load
If your page loads too slowly or has server errors, Googlebot might give up and not index it.
4. Thin or Duplicate Content
If your content is low-quality, too short, or copied from other sources, Google may skip indexing it.
5. Lack of Internal Links
Pages that aren’t linked to from other parts of your website are harder for Google to find and may be ignored.
To solve these problems, make sure your pages:
- Provide real value
- Load Pages quickly
- Aren’t blocked by technical settings
- Are included in your sitemap
- Have links pointing to them
How to Track Indexing with a Google Indexing Tool
To make sure your pages are being indexed, you need to monitor them. Luckily, you don’t have to do it manually.
You can use a Google indexing tool like:
1. Google Search Console
The official tool from Google. It lets you:
- Check if specific URLs are indexed
- Submit URLs for indexing
- View errors preventing indexing
2. Google Indexing Checker
If you’re managing multiple pages or websites, a third-party Google indexing checker ( like accuindexcheck ) can save time by:
- Checking multiple URLs at once
- Showing which pages are not indexed
- Highlighting pages with indexing errors
These tools are useful for webmasters, bloggers, agencies, and SEO professionals who need to stay on top of site performance.
Tips to Speed Up Google Indexing
Want your pages to be indexed faster? Follow these proven strategies:
- Submit URLs via Google Search Console
- Include new content in your XML sitemap
- Link new pages from existing, indexed ones
- Promote your content via social media or backlinks
- Fix crawl errors and avoid using “noindex” accidentally
- Keep your content original and useful
Final Thoughts
The Google indexing process is the foundation of SEO. Without indexing, your content doesn’t exist in search results — no matter how well it’s written or optimized.
If you’re unsure whether your content is indexed, use a Google indexing checker or Google Search Console to monitor it. If there are problems, fix them quickly using the tips above. And always remember: good content + clean structure + technical health = faster indexing.