
What Is Google Indexing and Why Its Important for SEO?
- accuindexcheck
- 0
- Posted on
If you’re working on a website, blog, or online business, understanding Google indexing is not optional — it’s critical. Without indexing, your content can’t appear in search results, which means no traffic, no visibility, and no growth.
This guide explains everything you need to know about Google indexing — in simple terms. We’ll walk you through:
- What indexing means
- How the Google indexing process works
- Why it matters for SEO
- How to check Google indexing status
- And how to fix common indexing issues
Let’s break it down clearly and thoroughly.
What Is Google Indexing?
Google indexing is the process by which Google adds your website pages to its search database.
Think of Google as a giant library. Indexing is like Google adding your web page to its “book collection.” Only after your page is indexed can it appear in Google search results when someone searches for a relevant topic.
If a page is not indexed, it will never appear in Google searches — no matter how great your content is.
Indexing vs. Crawling – What’s the Difference?
Many people confuse crawling with indexing, but they are two different steps:
| Term | What It Means |
|---|---|
| Crawling | Googlebot (Google’s web crawler) visits your website to discover pages. |
| Indexing | Google stores and processes those pages into its search database. |
✅ Crawling finds your page.
✅ Indexing remembers your page.
If your content is crawled but not indexed, it’s like Google knows it exists — but chooses not to show it.
When you create a new web page or blog post, Google doesn’t instantly know about it. Before your content can show up in search results, it must go through a four-step process:
1. Discovery – How Google Finds Your Content
The first step is discovery. This means Google has to find out that your page exists.
How does discovery happen?
Google finds your pages in several ways:
- Following a link from another website or from a page that’s already indexed.
- Reading your XML sitemap, which lists all the important pages on your site.
- Manual URL submission through tools like Google Search Console.
If Google doesn’t discover your page, it won’t go any further. Discovery is the entry point to the entire indexing process.
2. Crawling – When Google Visits Your Page
Once your page is discovered, Google sends out its crawler — called Googlebot — to visit the page. This step is called crawling.
During crawling, Googlebot scans the page and downloads its content. It reads:
- The main text and headlines
- Links to and from the page
- The layout and structure of the HTML code
- Scripts, styles, and other technical elements
If your site is slow, broken, or blocks Googlebot in your robots.txt file, crawling may fail.
3. Processing – When Google Analyzes Your Page
After crawling, Google begins processing the page. This is when it tries to understand the purpose and content of the page.
During processing, Google looks at:
- The words on the page and their meaning
- The structure of the content, including headings
- Images and their descriptions
- Page speed and mobile usability
- Whether the content is original or duplicate
- Technical SEO elements like canonical tags, meta descriptions, and structured data
If the page has good content, works well on all devices, and loads quickly, it moves to the next stage.
4. Indexing – Adding Your Page to Google’s Database
After processing, if Google determines that the page meets its quality standards, it will be added to the Google Index.
The index is Google’s searchable database. Only indexed pages can appear in search results.
If your page is blocked by a noindex tag, contains spam, or doesn’t offer value, Google may choose not to index it.
Once your page is indexed, you can track its performance in tools like Google Search Console, and it becomes eligible to rank for relevant keywords.
Now the page is eligible to rank in search results.
Why Google Indexing is Important for SEO
Now that we know what indexing is, let’s talk about why it’s vital for SEO.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) helps your pages rank higher in search results, but SEO only works if your page is in the index. If it’s not indexed, no one can find it via Google — even if you’ve written the perfect blog post.
Here’s why indexing matters:
- Visibility: Indexed pages can appear in Google Search.
- Performance Tracking: You can only track impressions, clicks, and rankings for indexed pages.
- Traffic Growth: More indexed content = more opportunities to rank.
- SEO Tools Access: Tools like Search Console, Ahrefs, and SEMrush rely on index status.
Without indexing, all your keyword optimization, backlinks, and content efforts are wasted.
How to Check Your Page Indexing Status on Google
If you want to know whether a specific page or your whole site is indexed by Google, here are three easy methods:
1. Google Search Method
Go to Google and type:
site:accuindexcheck.com
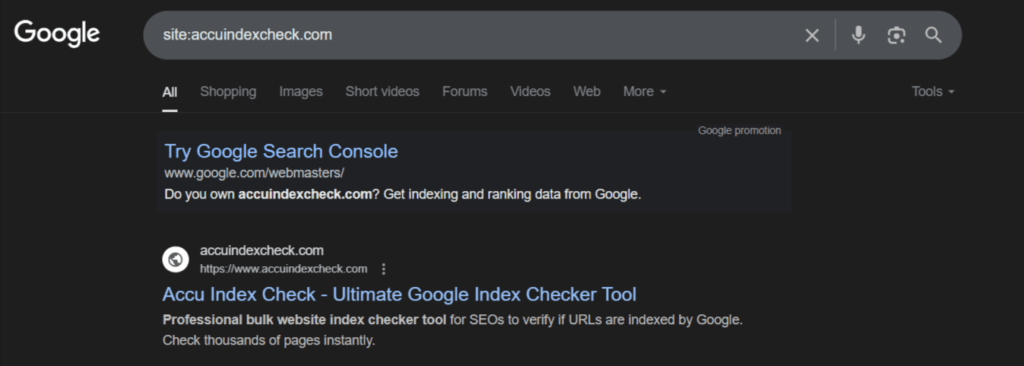
Example:
makefileCopyEditsite:blog.backlinkchecker.co
- If results appear: ✅ your site is indexed.
- If you see “Your search did not match any documents”: ❌ it’s not indexed.
2. Google Search Console
This is the most accurate way to check indexing status.
- Sign in at Google Search Console
- Select your property (site)
- Use the URL Inspection Tool to check specific pages
- See whether it’s:
- Indexed
- Crawled but not indexed
- Blocked
You can also request indexing directly from here.
3. Google Indexing Checker Tools
If you manage many pages, use a Google indexing checker (like the one on your site) to:
- Bulk-check URLs
- Monitor indexing issues
- See which pages are missing from Google
This is helpful for agencies, bloggers, or SEOs managing large sites.
Common Reasons Your Pages Aren’t Indexed
Here’s why some pages are not showing up in Google’s index:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Noindex Meta Tag | Tells Google not to index that page |
| Blocked by robots.txt | Prevents Google from crawling the page |
| Orphan Page | No internal links point to the page |
| Duplicate or Thin Content | Google skips low-value or repeated content |
| Slow Page Speed or Errors | Poor loading performance or broken code |
| Spammy or Low-Quality Content | Content that violates Google’s quality rules |
To ensure Google indexing your website is smooth, fix these issues first.
How to Get Your Website Indexed Faster
Want faster indexing? Here are proven methods:
1. Submit Your Sitemap
Use Google Search Console to upload your XML sitemap (yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml). This helps Google discover all your pages.
2. Request Manual Indexing
In Search Console, paste the URL into the URL Inspection Tool and click “Request Indexing.”
3. Create Internal Links
Link to new pages from existing, indexed ones. This helps Googlebots find them faster.
4. Use Social Media & Backlinks
Promote your content. More links = more chances for bots to find and index it.
5. Fix Crawl Errors
Check for broken pages or blocked resources in Search Console and resolve them.
Monitor Regularly with a Google Indexing Checker Website
Don’t just guess whether your pages are indexed. Use a Google indexing checker tool regularly to:
- Track your most important URLs
- See which pages drop out of the index
- Get alerts when something breaks
This way, you can act quickly and avoid losing rankings or traffic.
Final Thoughts
Google indexing is the foundation of your online visibility. If your content isn’t in the index, no one will find it — even if you rank #1 in your niche.
Whether you’re launching a new blog post or managing a full-scale website, always:
- Understand how the Google indexing process works
- Use tools to check Google indexing status regularly
- Ensure your Google indexing website setup is clean and error-free
Combine great content with indexing best practices, and your SEO efforts will start to pay off.