How Search Engines Use Structured Data to Index Content More Accurately
- accuindexcheck
- 0
- Posted on
Search engines crawl through a large volume of content on the web; however, they use structured data to interpret very specific details accurately. Structured data provides a clear and common way to state the intention behind text, images, etc., on a page. Precisely, this lets search engines put the content in their index with better organization and provides advanced search options such as rich snippets that increase visibility and relevancy in search results.
This article will talk about structured data, how it affects search engine indexing, and how it could be applied for better SEO results.
What Is Structured Data?
Structured data acts as one convention for encoding and offering information about web content so that search engines can efficiently process and understand it. Schema markup is the corresponding code that can be applied; most commonly, JSON-LD, Microdata, or RDFa is used to specify product information, dates for an event, article’s author, ratings, and so on. When the structured data is loaded onto a page, it leaves little-to-no ambiguity for the search engines as to what the content really means and how it must be treated; this helps it to be well indexed and gives a good appearance to your listings in search.
Structured data would mark the recipe page, title, ingredients, time to cook, and reviews. So the engine considers that recipe for rich results by highlighting it with images and sufficient key detail to help it stand out in search listings.
How Structured Data Works?
Structured data works by adding a layer of code onto your website that explains what is the meaning of the content as opposed to just telling what it is. This thereby helps search engines grasp the context of your pages better. Schema.org being a global structured data standard, it provides a shared vocabulary for ways of marking up various types of content-article, product, recipe, and event.
There are mainly three formats for adding structured data:
- Typically preferred by Google is JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data). This one puts the code inside a <script> tag either in the head or body of your HTML, thereby not interfering with the rendering of the page by the browser.
- Microdata – This one puts structured data right inside your HTML tags by adding specific attribute names to the elements. The data stays close to the actual content but can make HTML harder to read and edit.
- RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes): Almost like Microdata, RDFa attaches attributes to HTML elements, but it has fewer restrictions when linking data across different sources, serving well in situations with complicated datasets or interconnected mediated content.
Types of Structured Data
The schema type chosen is very important on how it influences the way your page appears in search results. Using Article schema, you can display headlines, authors, and publication dates as rich snippets. Product schema instead does that for price, availability, and ratings.
The most classic structured data types include the following:
- Articles & Blogs – These increase visibility for news and blogs by displaying the headlines, authors, dates, and images.
- Products – Show price, availability status, brand information, and reviews in search engine results pages.
- Recipes – Feature cooking time, ingredients, and ratings to be showcased in recipe carousels.
- Events – Highlight event name, date and time, and location for fast perusal by the end-user.
- Local Businesses – Share contact information, opening hours, and location to keep local SEO boosted.
How Structured Data Helps in Better Page Indexing
Structured data serves as a translator between websites and search engines. So, your contents may be merely read and not properly understood. When you impart meaning and context to your information, search engines can go through your pages quickly and accurately.
How It Improves Indexing
- Clarifies the purpose of the content: Search engines should have an exact understanding of whether they’re dealing with an event, recipe, product, or review page.
- Focuses on details: Specifying information about key attributes, such as price, date rating, and author, is necessary to ensure they aren’t misinterpreted.
- Maintains a Consistent Data Structure: That is how search engines directly scan and categorize your content.
- Helps Content to Be Eligible for Rich Results: Proper implementation of schema warms up a better possibility of having your pages rendered with the rich snippets that get much more visibility.
Key Benefits of Structured Data for Indexing
- Faster Content Discovery – If proper markup is utilized, it can assist in quickly getting new pages indexed.
- Better Ranking Potential – Although structured data is not a direct ranking factor, it certainly improves the presentation, which in turn improves the chances of people clicking through.
- Increased Search Visibility – Rich snippets grab attention more and tend to get impressions and clicks.
- Improved User Experience in SERPs – Users are engaged in receiving more detailed information on their front before they feel obliged to click on your listing, making the listing so much more appealing.
How to Implement Structured Data
Adding structured data can hugely benefit the understanding that search engines have of your content; however, it is crucial that it is done correctly. Develop each step with great care:
1. Choose the Right Schema Type
The very first step is to determine what schema markup most correctly describes your content. Different schema types exist for different categories such as Article, Product, Recipe, Event, LocalBusiness, and so on.
Go to schema.org and check the available types. Choose the one of the property that fits nearest to what your page is about. For example, if you are marking up your blog post, use Article or BlogPosting; Product is for an e-commerce product page. With the correct type chosen, it helps search engines interpret your data correctly.
2. Add JSON-LD Code to Your Website
After deciding the schema type, it is necessary to add the code to the page. Google recommends JSON-LD because it is easy to do without disrupting any other HTML structure.
You can either place the JSON-LD script inside the section or at the very end of the tag. First, take an example from schema.org and substitute all placeholder text with actual details like title, description, author, price, or location. This code informs the search engine of what each piece of information means.
3. Test Your Structured Data
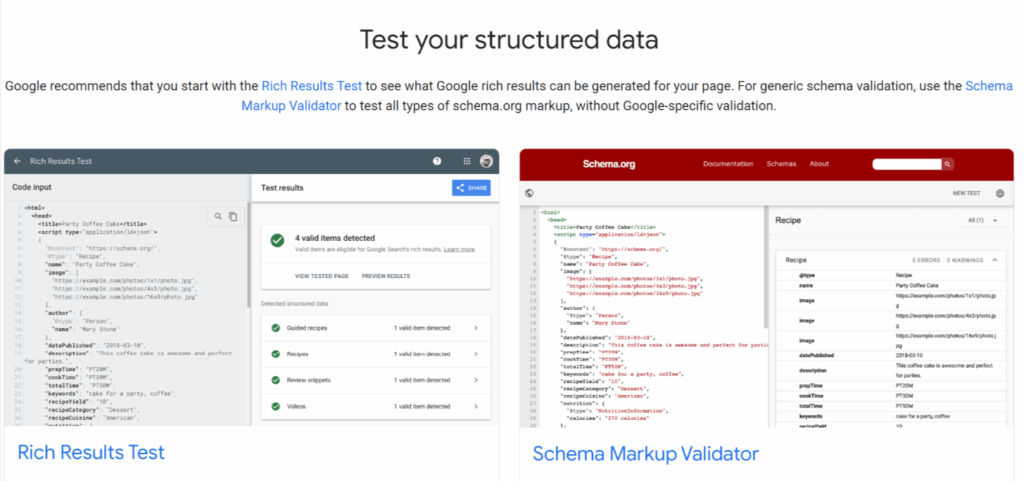
Test your structured data for errors before launching or even updating your page. You should run your code through either the Google Rich Results Test or Schema Markup Validator .
These checkers will alert you to any errors, missing fields, or warnings. Addressing these alerts before publishing ensures smooth data ingestion by search engines and eventual interference in indexing.
4. Keep Structured Data Updated
Structured data should always be able to correlate with what is actually present on the page. If you end up changing the title, or price, or date, etc., you also have to change the JSON-LD accordingly. Old or mismatched markup confuses search engines who then might go ahead and ignore the structured data. This freshness will therefore keep your rich snippets promoted in SERPs.
JSON-LD vs Microdata: Which Type of Structured Data Should I Use?
One of the most commonly used structured data formats is JSON-LD and Microdata. Both serve an identical function; they help search engines comprehend content better, yet each acts on its own; each has its set of pros and cons.
1. JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data)
- Google’s favorite format – JSON-LD has been officially recommended by Google for the implementation of structured data.
- Keep Separate From HTML – Keeping the JSON-LD structured data code enclosed within a script tag helps separate it with the HTML.
- Maintenance Friendly – In the event that you wish to add or update the information in the structured data, yet it will not affect any existing element of HTML or style rules, hence decreasing the odds of damaging the layout.
- Neater Source Code – It is never part of the HTML tag, so your source code stays cleaner and easier to debug.
Example Use Case:
If you take the example of an e-commerce site that wants to add product details such as product name, price, and availability, all the data about products can actually go into one JSON-LD block, instead of being specified in multiple HTML elements.
2. Microdata
- Inline Markup — One can consider it as being inseparably inserted into each HTML tag via attributes like itemtype and itemprop.
- Content & Code Together – It connects the structured data with an element of a visible page, which may complicate further updates.
- Better for Some CMS Templates — If your theme, for example, already supports Microdata, you might not be needing scripts anymore.
- Time-Consuming – A lot of Microdata changes require editing multiple HTML elements, getting problematic in bigger sites.
Example Use Case:
Microdata would be introduced into the <span> or <div> wrapping the author name in a blog post.
Which One Should You Use?
For most of the websites, JSON-LD is the best choice for implementation since it is easy to implement and maintain and is fully supported by Google. However, Microdata can be viable if your CMS or existing codebase already uses it, and conversion would entail heavy refactoring.
Why Structured Data Important for SEO
Structured data enhances how search engines perceive and display your content-aiding in higher ranks and rich results, giving a clear context for your pages, hence rendering the content more relevant and visible in search.
Here’s why it matters for SEO:
- Improves Search Engine Understanding : Structured data informs search engines about the detailed information of your content—whether it is a recipe, product, article, or event. The content is then categorized accordingly. This deeper understanding increases the chances of your content being shown to the right audience.
- Enables Rich Snippets and Enhanced SERP Features : Using markdown, your listing may include extra info like ratings, price, FAQs, or events on dates. These rich snippets give the listing a visual discrimination; therefore, they are more probable to enjoy a higher CTR.
- Enhances Content Discoverability : Structured data could be harnessed by search engines to display your content in special search features like Knowledge Graph, Carousel, or Featured Snippets to bring forth easy access to users.
- Facilitates Voice Search Optimization : Voice assistants like Google Assistant do their best to leverage structured data to ensure they deliver right answers. Therefore, implementing it will make your content relevant to voice search queries, a rapidly growing search trend.
- Better CTRs : Richer and more descriptive search listings always earn more clicks compared to the plain blue links. Higher CTRs signal search engines that your content is valuable, with possibly an indirect effect on the rankings.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Structured data implementation has to be done with accuracy. Even minute errors may prevent your pages from appearing in rich results. Some of the common errors that you should avoid include:
- Choosing the wrong schema type – The wrong or irrelevant schema may only confuse the search engines, which then choose to ignore your markup. Always try to select the schema type that best fits the content of your page.
- Incomplete or inconsistent markup – You weaken your structured data if you fail to provide certain required fields, or you provide information that contradicts the visible content. The search engines have to have this markup all in order to understand your page fully.
- Marking up content that is invisible to users – Google expects the structured data to mirror what is visible on the page. If something is marked but it is not visible, or if it is the wrong content, then penalties or reduced trust might come to bear.
Testing & Validating Structured Data
Check your structured data to make sure it has been implemented accurately and is eligible for a Google rich result. Using tools such as Google’s Rich Result Test, the Schema.org Validator, and Accu Index Check, errors can be detected, missing fields can be added, and it can be confirmed that search engines can read your data. Better indexing means a higher chance of your appearance in featured SERP attributes.
Something is wrong-make that correction right away-wrong property name, missing required attribute, invalid formatting. Updated testing of your markup should be carried out regularly so that it remains clean on search engines and is considered for better CTR.
FAQs
What data structure is indexing based on?
Search engines, Google especially, interact with various types of structured data such as JSON-LD, Microdata, and RDFa, to gather what websites give as information regarding their content and to interpret that information. This information is given to inform the crawlers so that they may know what kind of knowledge resides on a page and how pieces of that knowledge are interrelated.
Does structured data help with SEO?
Structured data is used in SEO for search engines to truly understand what your page is about. Price, dates of events, or names of authors are something to mention to increase the chances of your page getting featured on rich results and therefore receiving more click-throughs from users.
What is the difference between structured and unstructured data?
Structured data has a defined and machinable format wherein schema markup is often used to categorize the information. Unstructured data, by contrast, is raw information—like blog posts or videos—lacking a specific structure. The main difference is in the ease with which a search engine can process and comprehend the data.
What is structured data used for?
Structured data provides a description and label to the content of a website to allow search engines to feature it with an enhanced user interface in the search results. Therefore, it might display the ratings given by users to certain products, or the preparation time for a certain recipe, or even the schedule of a particular event. This serves to provide visibility to information and draw users’ attention by enriching search listings with useful information.
Why does Google use structured data?
Google uses structured data to draw a better interpretation and connection between pieces of content scattered around the web. The structured data help-the search engine to identify core elements, their relationships, and their contexts so that a richer search experience can be served to the users by combining carousels, FAQs, and quick answer boxes, thereby rendering the search results more relevant and visually appealing.
In Conclusion
Structured data assists the search engines in having an accurate understanding of your content and sharing it on relevant and enhanced search results. Selecting the right schema types for your content, such as articles, products, and local business details, directly impacts its visibility and CTR. Testing, validating, and continuously maintaining your markup guarantees that your SEO yields tangible results.