
How a Perfectly Designed Website Structure Elevates SEO Rankings
- accuindexcheck
- 0
- Posted on
Many websites also fail to rank well not because of their content, but due to their poor site structure. How your site is organized plays a big role in SEO success. A clean and well-organized layout benefits search engines crawling your content and provides smooth navigation for the users. An easy site to explore keeps visitors longer and decreases the bounce rate; Google appreciates it by providing a higher rank. This article will show you how the structure of your site will affect SEO directly and give you some really good tips on how to optimize it effectively.
What Does Website Structure Mean?
Website structure essentially refers to the way your content is arranged and connected. This involves navigation, internal links, categories of the pages, URL paths, and so forth. In the event of a good structure, it will be easier for users to find certain information, and it will enable search engines to go through the pages quite effectively. Well-chosen visibility is given to the concerned pages that will also significantly increase user engagement and SEO ranking. Website layout and architecture are like foundations of a house that support a user experience and search rankings for a long period.
Why Website Structure is Important for SEO
1. Improves Crawlability
The bots of search engines such as Googlebot need to scan your website to understand its content. The process through which bots scan the website is called crawling. A well-structured website presentation allows bots to glide through it with ease.
- If the structure is messy or if broken links abound, bots might be skipping entire pages or, worse yet, merely not understanding your content.
- A clean hierarchy and linking serve as a guide for the crawlers to the very core of your important pages.
For Example:
Whenever your homepage has a link to your blog while on the other side the blog is equipped with links to different articles, Googlebot simply crawls smoothly all through your content chain.
2. Boosts User Experience (UX)
An appropriate site structure assists one from getting lost or frustrated so that they can always get what they want quickly.
- Theoretically, a potential user should not be clicked on more than 2 or 3 times through a particular page from the homepage.
- Easy navigation encourages visitors to spend a few minutes more on your site and helps with bounce rate reduction.
Why it matters for SEO:
The search engine Google tends to give much attention to user signals. Higher bounce rates or low time spent on a site may signify poor quality, affecting rankings.
3. Strengthens Internal Linking
Internal linking pertains to linking pages within the same website. When your structure is organized, one can create such connections meaningfully.
- It has been observed that internal links pass on link equity, or SEO value, to other important pages:
- Internal links are also crucial for helping Google understand what the pages deal with and precisely how the pages are interconnected.
4. Enhances Site Hierarchy
A strong website structure forms a logical hierarchy starting from broad categories and penetrating into very specific content.
- It might look like so:
Homepage > Services > SEO Services > Local SEO - This hierarchy not only helps the users with the flow of the site but also helps search engines assign priorities to pages depending on depth and importance.
5. Supports Sitelinks in Search Results
Sitelinks are links that show up beneath your site on Google search results, belonging to a clean, structured environment.
- Google assigns sitelinks based on the layout and navigation clarity of your site.
- Sitelinks can increase your CTR due to their clickability and give your brand an amazing aura of credibility.
For Example:
If someone searches for “YourSiteName,” they might see:
www.yoursite.com
- About Us
- Services
- Blog
- Contact
6. Helps with Faster and Better Indexing
When a site is well structured, search engines adopt their flexibility and define which enhancing will be given as a result for an entered query.
- Indexing is the process Google stores information about your site to present in search results.
- If loose or ambiguous constructions impede the bots in indexing your practical pages, these limitations influence considerably toward delayed indexing.
- Anyhow, where any given page is not indexed, the page will not show up in Google results at all, albeit great is the content.
How Does a Good Site Architecture Appear?
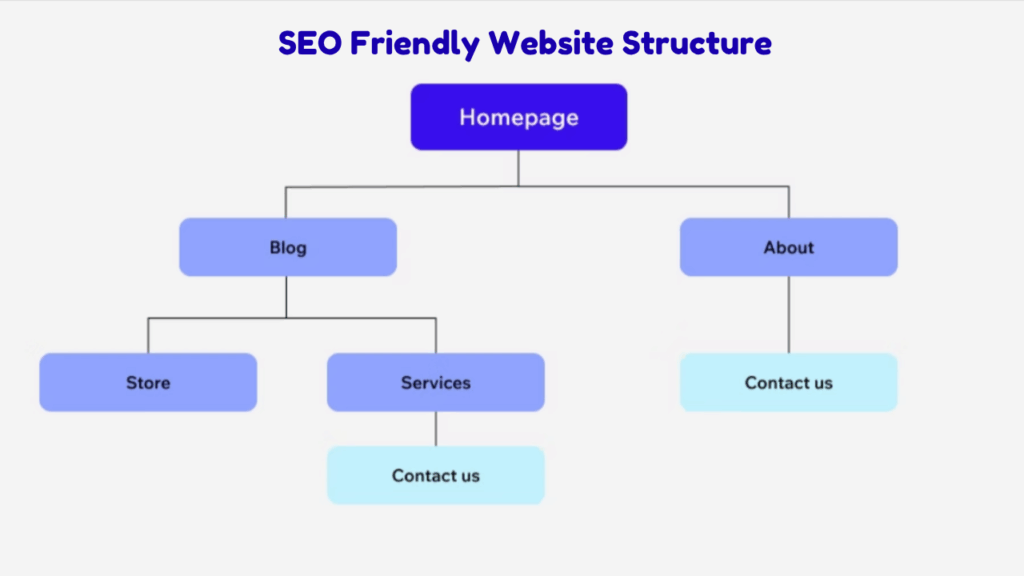
For the proper running of the website and better rank for the search engines, a layout that is user-friendly and search engine-friendly should be present.
- Group your website content so that similar topics are grouped together for optimized clarity.
- Any important page should, in theory, be two to three clicks away from the homepage for the user. Ensure that.
- Use internal linking from one relevant page to another to achieve both usability and proper navigation flow for the search engines.
- Make the URLs short and descriptive for what the page is all about.
- Avoid duplicate or similar content on multiple web pages since it can confuse visitors.
- Use breadcrumb navigation so that the visitor can retrace his or her steps and so that search engines may easily understand the page levels.
Effective Site Structure Strategies for Better SEO
1. Site Architecture and Hierarchy
Website structure describes how your different pages are interconnected and how their flow occurs. Meanwhile, if well structured, a search engine will be able to map out your most important pages and see collections thereof. In short, having transparent organization will greatly provide your site with a big chance of getting ranked well by emphasizing useful content in a logical order.
Best practices for site hierarchy:
- Design your site into layers: Home(main page)>Main Sections>Subsections>Individual Posts.
- Give special priority to your key content by linking to it often.
- Add breadcrumb links so that users can see where they are amidst the navigation.
2. Page Speed and Load Time
The loading speed of a website really can have a big effect on customer satisfaction- and visibility on search. A clean and well-organized site can keep the files tidy and cut down on redundant code, putting less pressure on your server. The smoother set-up then helps speed up page loading, thereby giving it a better browsing experience. Google promptly confirmed that faster pages rank above slower ones in search results.
To improve page speed:
- Enable image compression and lazy loading.
- Minimize JavaScript files and recombine scripts where necessary.
- Deliver content more rapidly using a CDN.
3. XML and HTML Sitemaps
XML sitemaps are bit like a road map guiding the search engines to all the important pages for discovery and indexing. If presented properly, it will ensure that the search engines understand the generic site architecture and do not omit crucial content. HTML sitemaps are meant primarily for the users-who may be needed to navigate large sites with ease.
Sitemap tips:
- Submitting an XML sitemap on Google Search Console is somewhat speeding up the indexing of new pages.
- Only submit canonical URLs to evade duplicate content issues.
- Put the HTML sitemap in the footer for easy accessibility for visitors.
- To put it simply, a sitemap update means adding or removing pages.
- If the sitemap has over 50,000 URLs or so, it will need to be split into smaller ones.
- Test whether your sitemap is required or not after its creation using tools like Screaming Frog, Yoast, and so on.
- Ensure that the sitemaps you want to submit do not include links that are “noindex” or broken.
4. Organising Your Website Content the Smart Way
Proper content grouping allows visitors to browse easily, and also allows Google to understand the site. This is known as “taxonomy”; it is a fancy word used for how your content is organized into categories and tags. When everything is just here and there, users can navigate only so far, but search engines might never see the important pages.
For that reason, it’s always great to segregate your content nicely. For instance, let’s say you have a blog or an ecommerce website: try not to overwhelm your site with random tags, vague categories, or categories that have nothing to do with the content. This in return helps in organizing your website that makes it a candidate for Google ranking.
Simple tips to keep things organised:
- Category names should be clear and brief so users instantly recognize what the category stands for.
- Do not use the same tag or category name twice — it might get search engines confused.
- The tags should only be assigned when they assist in grouping together related content.
- Place subcategories under the right parent category; “Laptops” go under “Electronics”.
- Keep checking, cleaning, old categories you no longer use.
5. What Are Orphan Pages and Why They Matter
Sometimes, a page on your website might not be linked from anywhere source: not from your homepage, menus, or other articles. Such pages are called orphan pages. Because they lack the crucial links, rarely do users and require search engines involved in their discovery. If they do not go into the sitemap manually, Google could potentially ignore these pages, making them absent in the search results.
Orphan pages tend to appear with every redesign or housekeeping carried out on the site. Therefore, it is imperative to regularly look into your site and check that all pages which have a purpose are somehow linked.
How to fix orphan pages:
- If the page still serves a purpose, fresh internal links should be given to it in the upcoming blog updates.
- Link to it naturally within other related articles or content pieces.
- If important, add it to the main menu, sidebar, or footer of the website.
- Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, and similar tools help to scan for pages having no internal links.
- Wherever they fit in an orphan page, keep them into content hubs or topic clusters.
- Add them to the HTML sitemap for easy crawling by search engines.
- Try to give a bit of consideration during the audit to old or neglected content, and then elect something, be it retention, updating, or deleting.
6. Why Headings Matter for SEO and User Experience
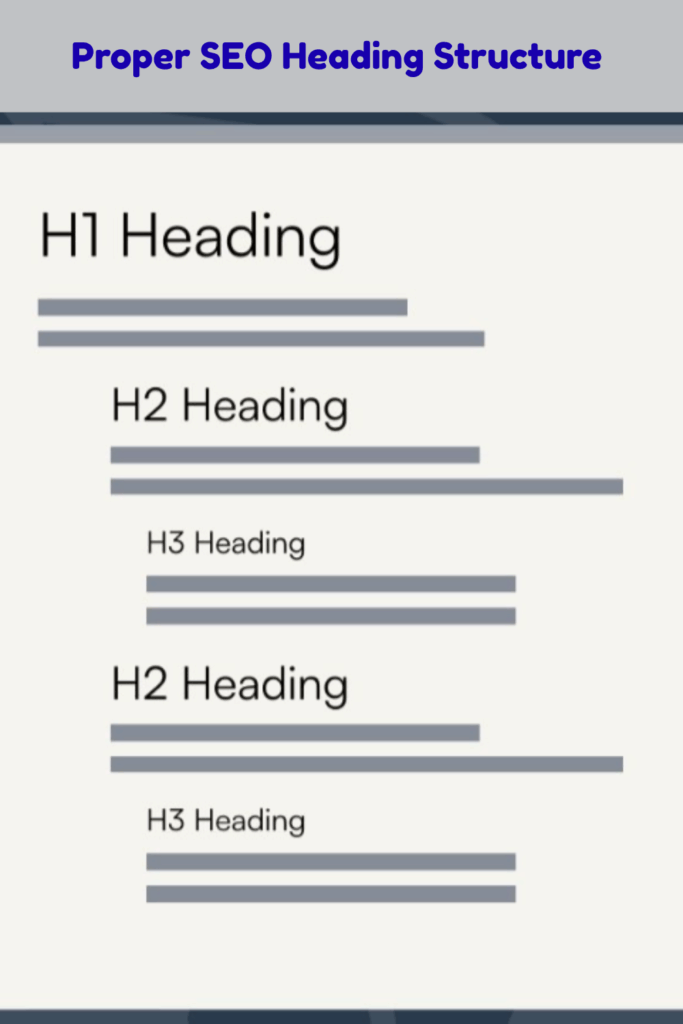
Your content becomes easier to read with proper use of headings. At the same time, the headings must convey to search engines how the information is organized within your content. They act as signposts for your readers as well as Google on the journey that comprises your page. When your headings are organized with a clear order and beneficial keywords, it boosts the SEO and user experience of the content.
Tips to make clean headings:
- In this respect, have them brief and easy to read.
- Only one H1 is permitted — the main title, presumably.
- Consider the H2 headings to be for major sections, with the H3s going underneath them for subtopics.
- Keywords should be sprinkled naturally throughout the headings.
- Do not skip heading levels (never go H2, then H4).
- Make the headings clear and relevant to the section content.
7. Optimize URL Structure and Slugs
A very prominent consideration to how people and search engines see a page is what comes after the slash: the slug. A tidy and straightforward URL gives visitors a clue about the page’s content even before they click. Search engines, too, look at URL keywords to know about the page confusion. In short, a URL rich in keywords that is easy to read helps with ranking and click-through rates.
Smart ways to structure your URLs:
- These are the few criteria that a good slug should meet. It must be rather short and precise, reflecting the actual content of the page.
- Words must be separated using hyphens (-).
- Do not put in any random numbers and symbols in your links.
- Maintain one structure throughout your site.
- Put in keywords if it feels like a natural thing to do.
- Try not to go for lengthy and complicated URLs that will probably turn away the user.
8. Mobile-Friendly Design Matters for SEO
Getting things responsive for mobile phones and tablets is a development that has gained importance over time. How your site is designed plays a very important role in its performance on smaller screens. Having an easy and practical layout on mobiles would always help site visitors access and interact with your content, irrespective of the device they use. Search engines recognize this and often grant greater visibility to the mobile-optimized site in mobile search results.
Tips for a mobile-friendly experience:
- Respond to a smooth layout for any possible screen size.
- Make buttons, menus, and links finger-friendly to focus on.
- A test of the site on multiple devices will help locate layout or usability issues.
- Never use small fonts or closely packed elements that could be annoying for mobile users.
- Ensure that images and videos scale down properly and never hamper load speed.
9. Website Structure Affects User Experience
A website’s interaction with people largely depends on its structure. If a site is well-organized and forced visitors to bothered getting what they came for, it’s a lousy setup. Give them clean layouts, easy menu navigation, and good internal linking to help them effortlessly glide through. If users can float through the website without any kind of terror, they tend to stay longer, browse more pages, and fare better in actions such as signing up or making a purchase.
Ways to improve UX through structure:
- Simplify the navigation system through meaningful page titles.
- Maintain a common layout on all pages.
- Create mutual links between related pages with clear and sincere anchor text.
- Avoid clutter. Let all the contents be easy to scan and read.
- Make key pages prominent for users to access them in minimum clicks.
10. Improve Breadcrumb navigation
Breadcrumb navigation is a simple trail showing the users their exact location within your website. Breadcrumbs not only ease browsing by allowing visitors to retrace steps back to earlier sections, but they also allow search engines to recognize the relationship among your pages.
Tips for using breadcrumbs smartly:
- Broader structured-markup needs to be incorporated to make top results appear cleaner and well-arranged in Google.
- Keep the label consistent with your menu name.
- Well-placed at the top for better viewability.
- Each breadcrumb-link has to be clickable and easy to follow.
FAQs
What is the website structure?
Website structure refers to how the pages of a website are arranged and interlinked. It consists of navigation menus, internal linking, url hierarchy, and content layout. A straightforward structure helps users and search engines locate and understand the content quickly.
Does website structure affect SEO?
Sure, website structure plays a large role in whatever SEO the developer wants to apply. A strong, good structure assists in crawling, provides more user satisfaction, works on link equity distribution, and finally, promotes indexing of crucial pages by search engines.
How to create a website structure diagram?
Start by listing your main pages and subpages. Arrange them in a flowchart showing what are parents and children; e.g., homepage > categories > subcategories > posts. Tools like Lucidchart, Figma, or even good old pen-and-paper would suffice for visualization.
What is Schema in a website?
Schema markup is a structured data markup which can make search engines better understand your content. It gives some extra info (e.g., ratings, product information, breadcrumbs) that appears as rich results on search engines.
What are the three basic website structures?
The three basic website structure types are:
- Hierarchical (Tree) – Pages are organized from broad to specific.
- Linear (Sequential) – One page leads to the next in a straight line.
- Network (Web-like) – Pages are highly interconnected with links across topics.
In Conclusion
If you want strong SEO and smooth user experience, first ensure the website structure is sound. Everything in the architecture of your site-from simplistic navigation, responsive design, URL optimization, internal linking-has a role in allowing its content to be easily accessible by users and search engines. By taking time to plan and maintain a logical structure, you not only improve your site’s visibility in search results but also keep visitors engaged and satisfied. Long-term prospects of sustaining online growth skyrocket as investments are made in smart website structure.