How to Fix the ‘Blocked by robots.txt’ Error in Google Search Console
- accuindexcheck
- 0
- Posted on
Maintaining search ranking remains a power behind attraction generation and site growth, but some unseen issues pull the site backward. One such instance comes into play wherein Google indexes a page that it should technically be banned from crawling. Hence, the message here-“Indexed, though blocked by robots.txt.”
In other words, the file robots.txt will forbid Google to access the pages directly but will still allow those pages to be listed in the search results. This deprives the search engine of its own job as providing such content to users is outside its purview.
Our guide will take the reader through a journey in detail to analyze the problem and explain how to find and identify it on one’s site and then very clearly and simply speak about the steps to take in fixing the issue so that the content can be crawled and indexed properly and much better for SEO purposes.
What Does ‘Blocked by robots.txt’ Mean in Google Search Console?
These messages, appearing on the GSC, indicate that for a given page, Google made a crawl attempt but was blocked by your robots.txt. The file is a kind of traffic controller that directs search engines from different areas of a website.
The other important thing is that even if the page content is blocked, it can be listed if other sites are linking to it. Basically, Google knows about the URL but cannot access the content; hence, the indexing is either partial or without any meta info.
This includes something like login forms, admin areas, or even duplicate content area. By understanding which URLs are blocked by your robots.txt file, you will be able to identify those pages that are probably, albeit unintentionally, keeping Google from getting a clear idea of your website’s structure.
Common Causes of the ‘Blocked by robots.txt’ Issue
Actually, a number of reasons can cause the “Blocked by robots.txt” error to appear inside the Search Console. The main ones are the following:
Robots.txt is Not Configured Properly
This is usually a robots.txt misconfiguration. Improperly used Disallow directives turn actual prohibited crawling into pages that actually get crawled by Google when those pages should never have been permitted. This happens most frequently when site owners themselves are confused regarding how the directives operate or enforce them in an overly generic way without testing. Essentially, with proper instruction, disallowing pages in certain large directories should even keep those pages indexable.
Too Broad Disallow Rules
Sometimes rules in robots.txt get too general, ending up disallowing more pages than should be disallowed. For example, in disallowing access to a directory, in effect it disallows access to all of its subfolders and files as well. Such broad rules can hamper SEO if they prevent search engines from pulling up eligible content from the rankings.
Outdated or Legacy Directives
Legacy robots.txt directives intended for an older generation of sites may not be applicable in modern times but would be rushing to block present-day content if unattended or unremoved. If a redesign or migration appears to have carried forward some of these antiquated indexing interfering rules, the file must be reviewed thoroughly.
Typos and Syntax Errors
The slightest slip of hand-any missing slash, one extra character, a wrong format-might totally change the intent of the directive, putting it into effect, hence barring the crawling of pages. So the tiniest of errors will block some very important parts of your site; hence this file must be read and tested holistically.
Unwilling Plugin Interference
What the SEO plugins or tools do is, in effect, edit the robots.txt file, sometimes inserting a new directive that blocks pages of vital importance to the webmaster, with the webmaster blissfully unaware of the blockage. These automatic changes might be contradicting manual settings made before, so it is really essential that one keeps track of rules brought about by the plugin, as well as any manual rule-change they make themselves.
How to Detect ‘Blocked by robots.txt’ in Google Search Console
Step 1: Sign in to Google Search Console
Log in with your Google account to access your website property. Make sure correct property, domain or URL prefix, is selected to get the accurate data.
Step 2: Select Pages Under Indexing
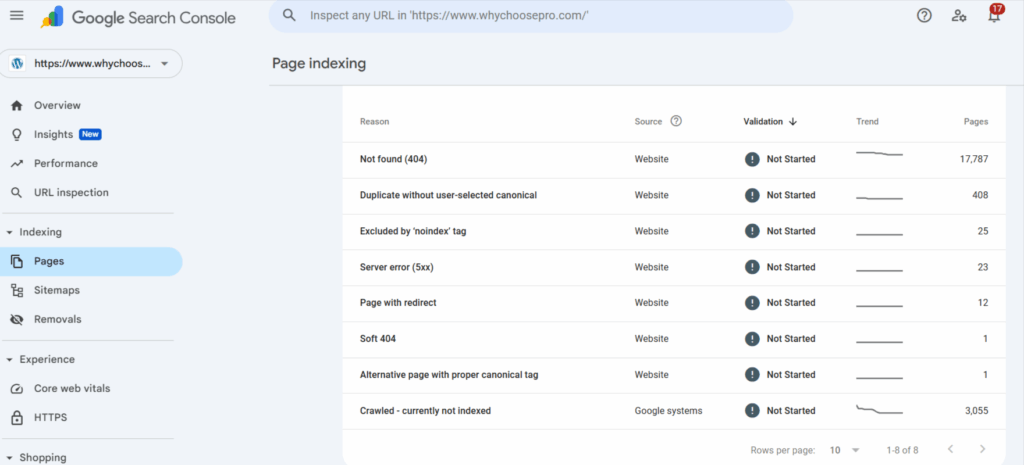
Go to Indexing → Pages from the left-side navigation. Here you get an overview of the URLs on the website and their indexing status.
Step 3: Look for Excluded Pages
Scroll down and check URLs with the Excluded status. These pages are not indexed for various reasons on behalf of Google—for example, they are blocked by robots.txt.
Step 4: Look for Blocked by Robots.txt
Check block methods for one named Blocked by robots.txt. This means that Google does know about this page but cannot crawl it because certain rules have been put in the robots.txt.
Step 5: Click on Inspect URL for Details
Clicking any blocked URL yields explanations and elaborations. One might view the last crawl date and the exact rule of robots.txt concerned from the blocking, which allows the user to decide whether it was an intended block or an accidental one.
Step 6: Run URL Inspection Tool
Enter one or more URLs in the URL Inspection Tool bar at the top of the console. If any robots.txt blocking issues exist, along with other problems with indexing or crawling, if any, they are listed.
Step 7: Periodic Assessment
Check the Pages and URL Inspection Tool routinely for new pages being blocked. This way, Google doesn’t end up with most important content blocked, and SEO continues its good work.
How to Fix the ‘Blocked by robots.txt’ Error
Making up for the Robots.txt :
Step 1: Locate Your robots.txt File
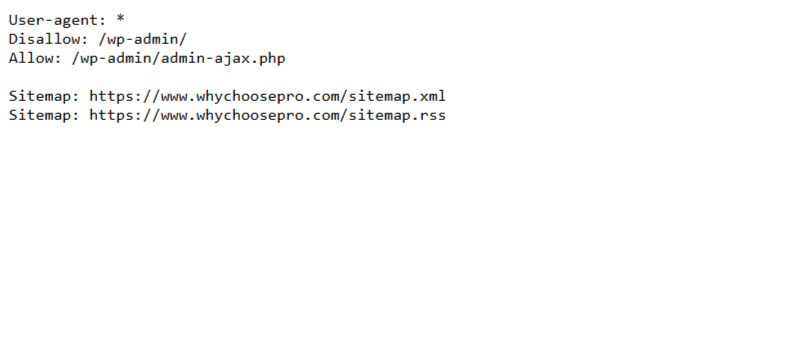
On any given website, this file sits inside the root folder (e.g., https://www.yourwebsite.com/robots.txt.trying to open that URL will give one an idea as to whether the file exists or is public).
Step 2: Check and Fix
Use your web host file manager or any available FTP client to access the robots.txt file. Read the instructions carefully as these beginning with “Disallow:” will make the search engine NOT to index the pages or folders stated after it.
If it seems too broad to you, fix it.
For instance: “Disallow: /” blocks the entire site; instead, block only specific paths.
Step 3: Save and Upload the File
Upload the file to the root directory once you’ve accounted for all the changes, replacing the old one.
Step 4: Confirm the Changes
With robots.md in place, visit https:/www.youramericanwebsite.com/robots.txt and forthwith check for various updates to see if they have taken effect.
Step 5: Testing in Google robots.txt Tester
Last but not least, do go into the Search Console and back into the robots.txt Tester to check for any errors or to make sure it has not disallowed any important pages. As those nodes get recrawled and reindexed, Google will hopefully update its perception of your site.”
Best Practices to Avoid ‘Blocked by robots.txt’ Errors
For proper management of your robots.txt file will prevent occasions where search engines will be prevented from accessing pages meant to be indexed.
1. Keep it simple and well organized
For the entire duration, a cleanly written and well-structured robots.txt file is a ghost for errors. Avoid complicated conditions or unnecessary instructions. Use comments in the script to justify why certain paths are blocked so that in the future, when reviewing or troubleshooting the file, it might be useful.
2. Use narrow Disallow directives.
Disallow only those pages or directories which need to be restricted rather than blocking a whole directory or using broad rules. Too generic a rule such as Disallow: / will block your entire site from crawling-a most unwanted consequence.
3. Get it reviewed and updated regularly
As time goes on, changes come to the website, and so changes to the robots.txt file occur too. Older rules should be relaxed and new ones added as appropriate to any kind of change in the site structure. Periodic review will ensure that legacy blocks do not interfere with any pages that are important.
4. Testing should precede changes.
You must test before you upload any changes using the Google robots.txt Tester or another tool. This testing ensures you do not block any valuable content by accident and that search engines can access and crawl those pages you actually want to be indexed.
5. Monitor industry reports in Google Search Console.
Keep an eye on pages or coverage reports in a Search Console because it helps to identify blocked URLs. Once detected, they may be fixed in no time, preventing damage to SEO.
6. Do not block crucial resources.
Avoid blocking CSS, JS, or any critical resources required for rendering the pages. Being able to access these files, Google can have a full grasp of your site layout, structure of contents, and other elements.
7. Be Careful When Using Wildcards and Sitemap References
Following by the book may make things easier for you, but it can bizarrely block several URLs. On the other hand, including your sitemap from robots.txt will help the search engines find the right pages efficiently.
Conclusion
Crawling and indexing problems arise due to a blocked by robots.txt issue for Google, and the same way will hamper your SEO.” After knowing the causes, checking the robots.txt file, and following the recommendations, important pages should be made available to the search engines. Periodic checks and care in handling your robots.txt will help know the good structure for your site and increase search performance as a whole.
FAQs
What could it mean to be blocked by the robots?
A blockage by robots on a page means Google’s crawling robots are effectively denied access to some page by an opposite disallowing rule in that website’s robots.txt. Sometimes the page may actually appear in the results because it might be linked from elsewhere, violating the prohibition.
Can we make an inaccessible robots.txt accessible?
Robots.txt may have not been found by Google for some time. First, one has to create the file. Does it really exist in the root directory? Type https://www.yoursite.com/robots.txt in the URL bar of your browser and check if it appears or not. Next comes the permission check. Provided there are no restrictions set, just go to The Google Search Console and test the robots.txt file before submitting it for re-crawling.
How to check if robots.txt is working or not?
Indeed! One could simply check using Google’s robots.txt tester, or just open up a browser and enter the line “https://www.yoursite.com/robots.txt.” The tester will check whether Googlebot “can theterior” (sic) access a certain URL from a list of URLs, responding by displaying one of two statuses applied to that particular URL: blocked or allowed.
How can one find that they were blocked by Googlebot?
The other Search Console tool is an URL Inspector. The initial use was to enter the URL of a page they wanted to inspect if it were being blocked by Googlebot through robots.txt. Then, it’s demonstrated when last it was crawled and if anything stood between it and being fully indexed.
Can robots.txt removal be done in Search Console?
Robots.txt implementation or removal is not performed by any tools inside Search Console; however, the Search Console will permit fixing crawling of the resources that these robots.txt files were denying. In any case, such blocking directives ought to be removed. Once changes are saved, the new copy should be uploaded to the root directory of the site.